Search results
Search for "minor groove binding" in Full Text gives 9 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Phenanthridine–pyrene conjugates as fluorescent probes for DNA/RNA and an inactive mutant of dipeptidyl peptidase enzyme
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 550–565, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.40

- and Phen-Py-2 with biomolecules Conjugates Phen-Py-1 and Phen-Py-2 were examined for DNA/RNA binding affinity and eventual preference for different polynucleotide structures. For example, the B-helical structure had a well-defined minor groove which is suitable for minor groove binding, while A
Selected peptide-based fluorescent probes for biological applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2971–2982, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.247

- 4 binds with dsDNA in a combined intercalation and minor groove binding mode, whereas probe 5 binds with the outer surface of dsDNA. These two probes are low cytotoxic and probe 4 has been successfully used for imaging of nuclear DNA (Figure 5B, inset). Protein detection Specific peptides and
Naphthalene diimide bis-guanidinio-carbonyl-pyrrole as a pH-switchable threading DNA intercalator
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2201–2211, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.185

- -DNAs only at pH 5, while at neutral conditions (pH 7) NDI-GCP2 switched to the DNA minor groove binding. Intriguingly, NDI-GCP2 was at both pH values studied bound to the ds-RNA major groove, still showing a higher affinity and thermal denaturation effect at pH 5 due to GCP protonation. At excess over
- threading intercalation into ds-DNAs at pH 5, while compound 4 at neutral conditions (pH 7) switched to the DNA minor groove binding. As often observed for threading intercalators, compound 4 was selective toward GC-DNA. Intriguingly, compound 4 was at both pH values bound to the ds-RNA major groove, most
Photocontrolled DNA minor groove interactions of imidazole/pyrrole polyamides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 60–70, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.8
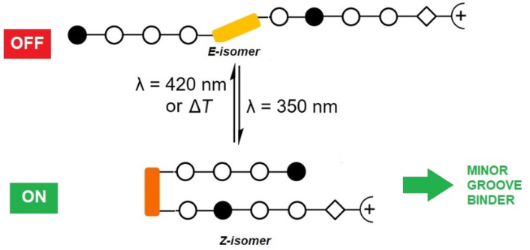
- compounds have frequently been employed as modules, e.g., to control protein–DNA interactions. However, their use in conjunction with minor groove-binding imidazole/pyrrole (Im/Py) polyamides is yet unprecedented. Dervan-type Im/Py polyamides were equipped with an azobenzene unit, i.e., 3-(3-(aminomethyl
- )phenyl)azophenylacetic acid, as the linker between two Im/Py polyamide strands. Only the (Z)-azobenzene-containing polyamides bound to the minor groove of double-stranded DNA hairpins. Photoisomerization was exemplarily evaluated by 1H NMR experiments, while minor groove binding of the (Z)-azobenzene
- acted as a building block inducing a reverse turn, which favored hydrogen bonds between the pyrrole/imidazole amide and the DNA bases. In contrast, the E-configured polyamides did not induce any ICD characteristic for minor groove binding. The incorporation of the photoswitchable azobenzene unit is a
An overview of recent advances in duplex DNA recognition by small molecules
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1051–1086, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.93

- considered similar to a standard lock and key recognition [30]. Minor groove binding drugs (MGBs) are usually isohelical, crescent-shaped molecules, which are compatible with the shape of the minor groove. Binding of MGBs and proteins occurs primarily via H-bonds, electrostatics, van der Waals and
- bond between the Im nitrogen and the exocyclic amine of guanine. Dervan et al. have further developed rules for base pairing recognition of minor groove binding polyamides where antiparallel side-by-side pairings of pyrrole (py) and imidazole (Im) amino acids successfully distinguish G·C from C·G base
- repeated DNA sequences in living cells were nicely visualized. Choice of fluorophores attached to the N-terminus of the polyamides remains extremely crucial, as they seem to affect DNA minor groove binding significantly. In order to design a novel DNA cleaving agent, a bis(guanidinium)alcohol tethered with
Polarization spectroscopy methods in the determination of interactions of small molecules with nucleic acids – tutorial
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 84–105, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.5

- , strongly supports minor groove binding to DNA or major groove binding to ds-RNA (Figure 7, blue hue). Exciton-coupled bisignate ICD bands: The appearance of exciton-coupled bisignate ICD bands (see chapter 2.1. and Figure 3, top) strongly support the aggregate binding along the polynucleotide, in which the
Come-back of phenanthridine and phenanthridinium derivatives in the 21st century
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 2930–2954, doi:10.3762/bjoc.10.312

- improved synthetic approaches. Keywords: ds-DNA and ds-RNA binding; intercalation; minor groove binding; nucleic acids; organic synthesis; phenanthridine; phenanthridinium; Introduction The search for therapeutic agents of the phenanthridine type has increased when the outstanding trypanocidal activity
- between various DNA and RNA polynucleotides was attributed to the switch of the binding mode (intercalation into dGdC-DNA and AU-RNA and minor groove binding into dAdT-DNA). A common strategy for the modification of DNA- and RNA-targeting molecules by preparation of homo-dimers was also implemented on the
- interactions between two phenanthridinium subunits and consequently their DNA- and RNA-binding mode (shorter linker–minor groove binding, the longest linker–intercalation) [66][67]. In addition, the derivative with the longest linker was, to the best of our knowledge, the first bis-phenanthridine-based
Molecular recognition of AT-DNA sequences by the induced CD pattern of dibenzotetraaza[14]annulene (DBTAA)–adenine derivatives
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 2175–2185, doi:10.3762/bjoc.10.225

- recognition; circular dichroism; DBTAA-adenine conjugate; ds-DNA/RNA; minor groove binding; nucleic acids; Introduction The majority of natural and artificial applications involving small molecule-DNA/RNA recognition depend on several non-covalent binding modes. Typical examples are double-stranded (ds) DNA
(Pseudo)amide-linked oligosaccharide mimetics: molecular recognition and supramolecular properties
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2010, 6, No. 20, doi:10.3762/bjoc.6.20
- studies showed that hybridization of DNG-Hoechst conjugates 64 and 65 to dsDNA enhances the stability of the triple helix through simultaneous minor groove binding by the tethered Hoechst 33258 ligand. Furthermore, Hoechst 33258 is able to enhance the stability of the duplex DNG·DNA with a flexible minor






























































































































































